Ansible Playbooks for Proxmox and LXCs Part 3
Ansible Playbooks for Proxmox and LXCs - Part 3#
In this episode, we’re finally going to get into the LXC we’ve created and start configuring it with Ansible. We’ll add it dynamically as a host, SSH into it, install some software, and more.
Adding a Dynamic Host#
In my last post, I outlined a strategy for acquiring the dynamically assigned IP address from the LXC once it’s been spun up. Now, we need to add that IP address to our Ansible hosts. In roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/main.yml, add the following:
- name: Add container to dynamic inventory if initial_setup is true
add_host:
name: "lxc_{{ container.vmid }}"
groups: proxmox_containers
ansible_host: "{{ container_ip }}"
ansible_connection: ssh
ansible_user: root
ansible_ssh_private_key_file: "{{ container.private_key }}"
ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
container: "{{ container }}"
when: container.initial_setup | default(false) and container.get_ip | default(false)
Our default Ansible configuration executes everything on localhost. This task adds a new host for Ansible. Let me explain:
groups- The host is added to a group calledproxmox_containers. The second play in our playbook, which I’ll describe shortly, will perform tasks on all hosts within this group. If you’re spinning up multiple LXCs and want them all set up, they’ll be added here.ansible_host- The IP of our newly provisioned VM, so Ansible knows where to connect.ansible_connection- We will connect overssh.ansible_user- We will connect as therootuser.ansible_ssh_prvate_key_file- This specifies the private key corresponding to the public key we uploaded.ansible_python_interpreter- This tells Ansible to use the default location for Python (i.e.,/usr/bin/python3) on the container, rather than trying to use the path from our local virtual environment.container- This passes all the container parameters from the controller to the host.
This task is contingent on the initial_setup and get_ip flags being set to true.
The Setup Script#
I’ve always used this relatively unsophisticated setup script to provision my new VMs.
#!/bin/bash
# Check if username and password were provided
if [ "$#" -ne 2 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <username> <password>"
exit 1
fi
USERNAME=$1
PASSWORD=$2
# Update and upgrade packages
apt update && apt upgrade -y
# Create the user, skip the contact info prompts, and assign the provided password
adduser --gecos "" "$USERNAME" --disabled-password
echo "$USERNAME:$PASSWORD" | chpasswd
# Add user to sudo group
usermod -aG sudo "$USERNAME"
# Install sudo if not installed
apt install sudo -y
# Confirm user creation
echo "User $USERNAME successfully created."
# Prompt to copy SSH key and wait for user to press Enter
echo "Please run 'ssh-copy-id $USERNAME@$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}')' from your host machine."
read -p "Press <enter> when done."
# Modify the sshd_config file to enable PubkeyAuthentication and disable PasswordAuthentication and root login
sed -i 's/^#PubkeyAuthentication yes/PubkeyAuthentication yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sed -i 's/^#PasswordAuthentication yes/PasswordAuthentication no/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sed -i 's/^#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password/PermitRootLogin no/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# Restart SSH service
systemctl restart ssh
# Retrieve the local IP address for the eth0 interface and display it
IP_ADDRESS=$(ip -o -4 addr show dev eth0 | awk '{print $4}' | cut -d/ -f1)
echo "Local address: $IP_ADDRESS"
# Prompt to press Enter before logging out
read -p "Press <enter> when done."
# Log out of the current session
logout
I want to achieve the following with Ansible:
- Update my sources and upgrade my packages.
- Add a non-root user.
- Install sudo.
- Add my new user to the sudo group.
- Assign a public key to that user.
- Enable pubkey authentication, disable password authentication, and disable root login.
This is the most rudimentary baseline setup for a Debian box. To translate this into Ansible, I’ve added the following tasks under roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/setup.yml:
- name: Update apt cache and upgrade packages
apt:
update_cache: yes
upgrade: dist
become: yes
- name: Ensure sudo is installed
apt:
name: sudo
state: present
become: yes
- name: Create non-root user
user:
name: "{{ container.username | default('demo') }}"
shell: /bin/bash
create_home: yes
password: "{{ container.user_password | default('demo123') | password_hash('sha512') }}"
become: yes
- name: Add user to sudo group
user:
name: "{{ container.username | default('demo') }}"
groups: sudo
append: yes
become: yes
- name: Copy SSH public key to demo's authorized_keys
authorized_key:
user: "{{ container.username | default('demo') }}"
state: present
key: "{{ lookup('file', container.pubkey_file) }}"
become: yes
- name: Ensure PubkeyAuthentication is enabled in sshd_config
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^#?PubkeyAuthentication'
line: 'PubkeyAuthentication yes'
become: yes
- name: Ensure PasswordAuthentication is disabled in sshd_config
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^#?PasswordAuthentication'
line: 'PasswordAuthentication no'
become: yes
- name: Ensure PermitRootLogin is disabled in sshd_config
lineinfile:
path: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
regexp: '^#?PermitRootLogin'
line: 'PermitRootLogin no'
become: yes
- name: Restart SSH service
service:
name: ssh
state: restarted
become: yes
Installing passlib#
The password hashing requires the passlib Python module. To install it, update your bootstrap.yml file to include:
- name: Bootstrap dependencies
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Install required Python libraries
ansible.builtin.pip:
name:
- proxmoxer
- requests
- passlib # Install passlib for hashing
state: present
Then, run:
ansible-playbook bootstrap.yml
Adding the Setup Play to the Playbook#
Back in our manage-lxcs.yml playbook, we need to add a new play.
---
- name: Manage Proxmox LXC containers
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: no
# Load credentials and LXC definitions
vars_files:
- ../vars/proxmox-vault.yml
- ../vars/lxcs.yml
tasks:
- name: Process each LXC container
include_role:
name: proxmox_lxc
loop: "{{ lxcs }}"
loop_control:
loop_var: container
# Add this part below
- name: Run initial setup on provisioned containers
hosts: proxmox_containers
gather_facts: yes
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Run initial setup tasks inside container
include_tasks: ../roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/setup.yml
This play will only run on hosts in proxmox_containers (the group we talked about earlier), so if there are no containers in this group, it won’t do anything.
Disable Host Key Checking#
If you want to stop the interactive prompt that asks whether you want to add an unknown host to your hosts file, add the following to your ansible.cfg file:
[defaults]
inventory = inventory
roles_path = roles
host_key_checking = False # This one
Modifying the LXC Manifest#
Back in lxcs.yml, we now want to test the whole shebang—spinning up an LXC from scratch and automatically performing the setup. That looks like this, with our new flags:
lxcs:
- vmid: 115
hostname: test06
ostemplate: "local:vztmpl/debian-12-standard_12.7-1_amd64.tar.zst"
storage: "local-lvm"
cores: 1
memory: 1024
swap: 512
disk: "local-lvm:25"
net: "name=eth0,bridge=vmbr0,ip=dhcp"
password: "containerpassword"
onboot: true
pubkey_file: "~/.ssh/nuc_rsa.pub"
state: present
- vmid: 115
hostname: test06
username: demo # Username for your non-root user on the VM
user_password: "demo123" # Password for your non-root user on the VM
pubkey_file: "~/.ssh/nuc_rsa.pub"
private_key: "~/.ssh/nuc_rsa" # Needed for Ansible to SSH
state: started
wait_for_status: true # Wait for the container to properly spin up
get_ip: true # Necessary for doing the initial setup
initial_setup: true # New flag
Now let it rip:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file vars/.proxmox-vault-pass playbooks/manage-lxcs.yml
Ansible will produce a whole odyssey of output. Here’s just the tail end:
TASK [proxmox_lxc : Debug - Show container IP] *******************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [localhost] => {
"msg": "Container IP is: 192.168.1.195"
}
TASK [proxmox_lxc : Add container to dynamic inventory if initial_setup is true] *********************************************************************************************************
changed: [localhost]
PLAY [Run initial setup on provisioned containers] ***************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *******************************************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [lxc_115]
TASK [Run initial setup tasks inside container] ******************************************************************************************************************************************
included: /home/demo/github/sbarbett/proxmox-ansible/roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/setup.yml for lxc_115
TASK [Update apt cache and upgrade packages] *********************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Ensure sudo is installed] **********************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Create non-root user] **************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Add user to sudo group] ************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Copy SSH public key to demo's authorized_keys] *************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Ensure PubkeyAuthentication is enabled in sshd_config] *****************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Ensure PasswordAuthentication is disabled in sshd_config] **************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Ensure PermitRootLogin is disabled in sshd_config] *********************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
TASK [Restart SSH service] ***************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [lxc_115]
PLAY RECAP *******************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=13 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=9 rescued=0 ignored=0
lxc_115 : ok=11 changed=9 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Everything ran without a hitch, so now I should be able to log in to my test container as the non-root demo user and verify:
❯❯ /home/demo/github/sbarbett/proxmox-ansible : ssh -i ~/.ssh/nuc_rsa demo@192.168.1.195
Linux test06 6.8.12-7-pve #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC PMX 6.8.12-7 (2025-01-17T08:18Z) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
demo@test06:~$ sudo apt update
[sudo] password for demo:
Hit:1 http://security.debian.org bookworm-security InRelease
Hit:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm InRelease
Hit:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm-updates InRelease
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
All packages are up to date.
demo@test06:~$ sudo apt upgrade
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
Calculating upgrade... Done
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
demo@test06:~$ cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep "PubkeyAuthentication yes"
PubkeyAuthentication yes
demo@test06:~$ cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep "PasswordAuthentication no"
PasswordAuthentication no
demo@test06:~$ cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep "PermitRootLogin no"
PermitRootLogin no
What a time to be alive.
Setting Up Passwordless Sudo#
I want to install some extra utilities using an additional flag. We’ll do this as the user we’re creating. First, let’s add a step to our initial setup that enables passwordless sudo for our user:
- name: Allow user passwordless sudo
copy:
dest: "/etc/sudoers.d/{{ container.username | default('demo') }}"
content: "{{ container.username | default('demo') }} ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL\n"
owner: root
group: root
mode: '0440'
become: yes
I put this right after the step that adds the user to the sudo group. You could probably just pass the password along, but this was simpler—and I wanted to give the user passwordless sudo anyway.
Add a Connection Test to Playbook#
Since part of the initial setup process disables the root user, subsequent runs with this flag enabled will fail if we try connecting as root. So I added a check at the beginning of the setup play to skip it if the root connection fails:
- name: Run initial setup on provisioned containers
hosts: proxmox_containers
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Test connection as root
wait_for_connection:
timeout: 15
ignore_errors: yes
register: root_conn_test
- name: Debug root connection test result
debug:
var: root_conn_test
- name: Skip initial setup if root connection fails
meta: end_play
when: root_conn_test.failed
- name: Run initial setup tasks inside container
include_tasks: ../roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/setup.yml
Add a New Non-root Host#
In your main.yml file under your tasks, we need to register a new host for the extras setup. Since root login is disabled after the initial setup, we’ll add a second host entry so that we can log in as the non-root user. After the initial baseline config, we perform the rest of our configuration using that user:
- name: Add container to dynamic inventory for extras setup
add_host:
name: "lxc_{{ container.vmid }}_user"
groups: proxmox_containers_extras
ansible_host: "{{ container_ip }}"
ansible_connection: ssh
ansible_user: "{{ container.username | default('demo') }}"
ansible_ssh_private_key_file: "{{ container.private_key }}"
ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
container: "{{ container }}"
ansible_become: yes
ansible_become_method: sudo
when: container.install_extras | default(false) and container.initial_setup | default(false)
This task adds the container to a group (proxmox_containers_extras) that a separate play (targeting that group) will use for extras configuration. That play will log in as the non-root user and perform additional configuration.
Add a New Task File for Extra Installs#
I created a new file under roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/extras.yml with the following.
---
- name: Update apt cache and install extra packages
apt:
update_cache: yes
name:
- kitty-terminfo
- tmux
- htop
- curl
- jq
- fzf
- neofetch
state: present
become: yes
- name: Backup update-motd.d and create new directory
shell: "mv /etc/update-motd.d /etc/update-motd.d.bak && mkdir /etc/update-motd.d"
become: yes
- name: Truncate /etc/motd
shell: "truncate -s 0 /etc/motd"
become: yes
- name: Create a .hushlogin file
shell: "touch ~/.hushlogin && chmod 644 ~/.hushlogin"
become: yes
- name: Append neofetch block to .bashrc
blockinfile:
path: "/home/{{ container.username | default('demo') }}/.bashrc"
marker: "# {mark} NEOFETCH BLOCK"
block: |
# Run neofetch only in interactive shells
case $- in
*i*)
echo " "
neofetch
echo " "
;;
*) ;; # Do nothing for non-interactive shells
esac
become: yes
become_user: "{{ container.username | default('demo') }}"
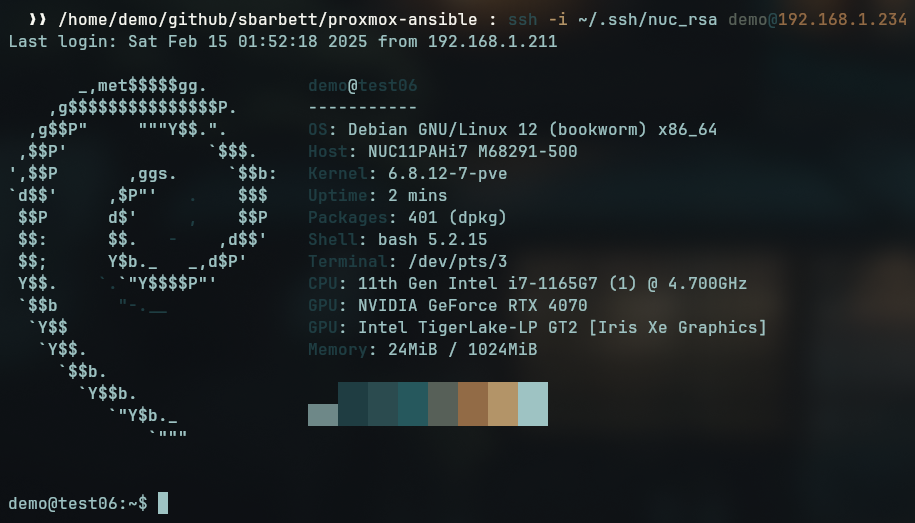
This will:
- Install some basic utility packages via
apt(feel free to add or remove from the list). - Silence the
motdand other default login messages. - Add a small block to
.bashrcthat will runneofetchat login (I dunno, I like this because I thinkneofetchlooks cool).
Update Playbook & lxcs.yaml#
Finally, in your playbook add the following play:
- name: Run extras setup on provisioned containers (non-root)
hosts: proxmox_containers_extras
gather_facts: yes
tasks:
- include_tasks: ../roles/proxmox_lxc/tasks/extras.yml
Then, in your lxcs.yml file, add install_extras: true after your initial_setup: true line. Run your playbook and log in to your LXC to see if it successfully installed the software.
Closing#
That’s all I have in me for today. I have some more ideas, so there will be a part 4 where we get into installing Docker, creating tasks for provisioning pre-configured containers using compose files, and maybe even putting them behind a reverse proxy (Traefik). As usual, the latest updates are on GitHub. ‘Til next time.